Files and File System
Everything is a file
A file is an addressable location that contains some data which can take many forms.
-
Text data
-
Binary/Image data
Files have associated meta-data
-
Owner
-
Group
-
Timestamps
-
Permission:
- Read(r)
- Write(w)
- Execute(x)
- no permission(-)
File permissions

File names
-
Case-sensitive: myfile.txt is different from MyFile.txt.
-
Hidden files: Filenames starting with a dot (.) are hidden by default.
-
File extensions: Not mandatory, but using them helps identify file types.
-
Spaces: Allowed but not recommended, use _ or – instead.
Best practices of file names
-
Keep names descriptive and concise.
-
Use lowercase for consistency.
-
Avoid special characters unless necessary.
-
Stick to alphanumeric characters, underscores, and hyphens.
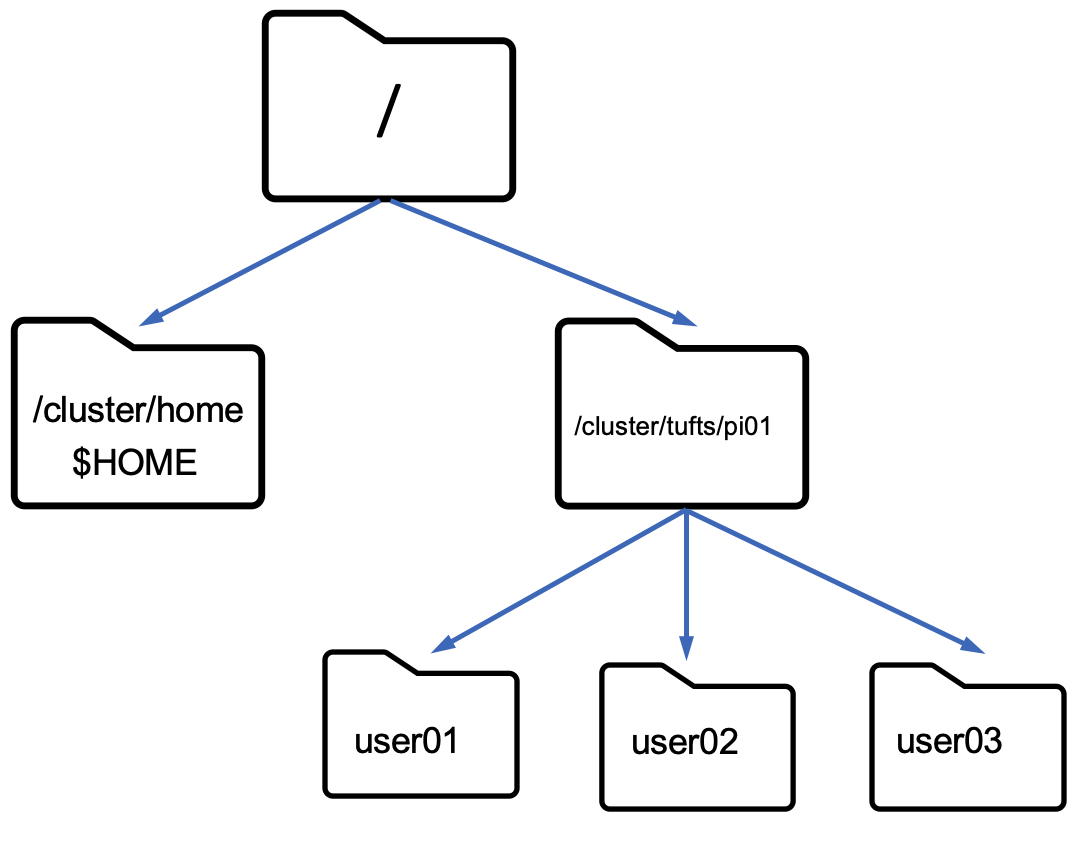
File organization
Everything is mounted to the root directory
Files are referred to by their location called path
-
Absolute Path (From the root): /cluster/tufts/mylab/user01
-
Relative Path (From my current location):user01